Kenya’s Tana River Delta Ramsar Site Launched
-
Coastal resilience
-
Coastal wetland conservation
-
Rivers and lakes
To celebrate World Wetlands Day 2014, Kenya’s Tana River Delta Ramsar Site was officially launched with a public celebration attended by over 500 people.
Encompassing 163,600 hectares, the Tana River Delta Ramsar Site was officially established in October 2012. The Tana is Kenya’s 6th Ramsar Site and the only Ramsar wetland outside the Rift Valley.
Stakeholders, including the communities, governments and NGOs worked together for six years to designate the site.

To celebrate World Wetlands Day 2014, the Tana Ramsar site was officially launched with a public celebration in the delta.

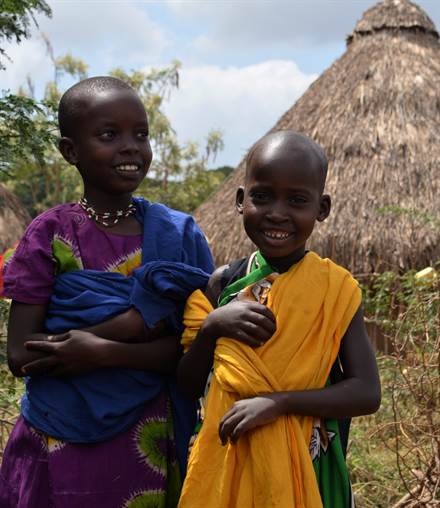
There are 16 tribes and 106 villages in the Tana River Delta and well over 500 people attended from across the region to celebrate the event…

…with speeches…

…and songs and dance
The Tana Ramsar site supports outstanding nature, including several threatened and endangered species of marine turtles, monkeys and the African elephant. The delta supports tens of thousands of wetland birds, making it one of the key sites in the country for waterbird conservation.

The Tana is the second most important estuary and delta ecosystem in Eastern Africa, with a variety of outstanding freshwater, floodplain and coastal habitats.

The Tana is the most important river in Kenya. However, the climate is getting drier.

There is decreasing water availability in the Tana Delta and growing water demand upstream.
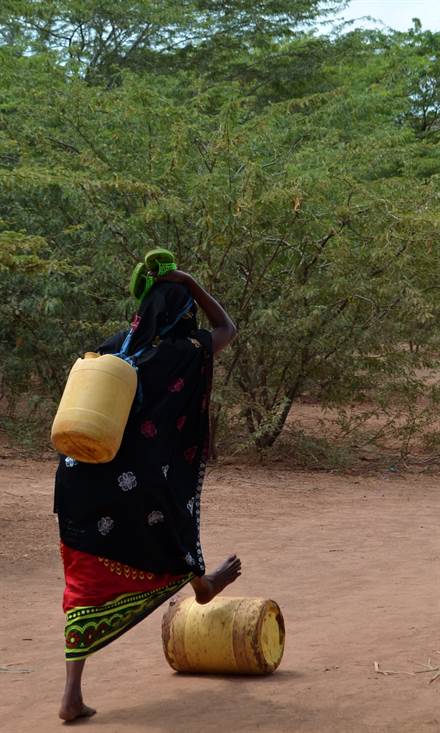

Livelihoods here consist of pastoralism, farming and fishing.

Wetlands International is working together with Both ENDS and IUCN NL with funding from the Dutch government for the sustainable management of wetlands and water resources in the Tana River Delta in order to preserve the rich ecosystems and the people who depend on them.

